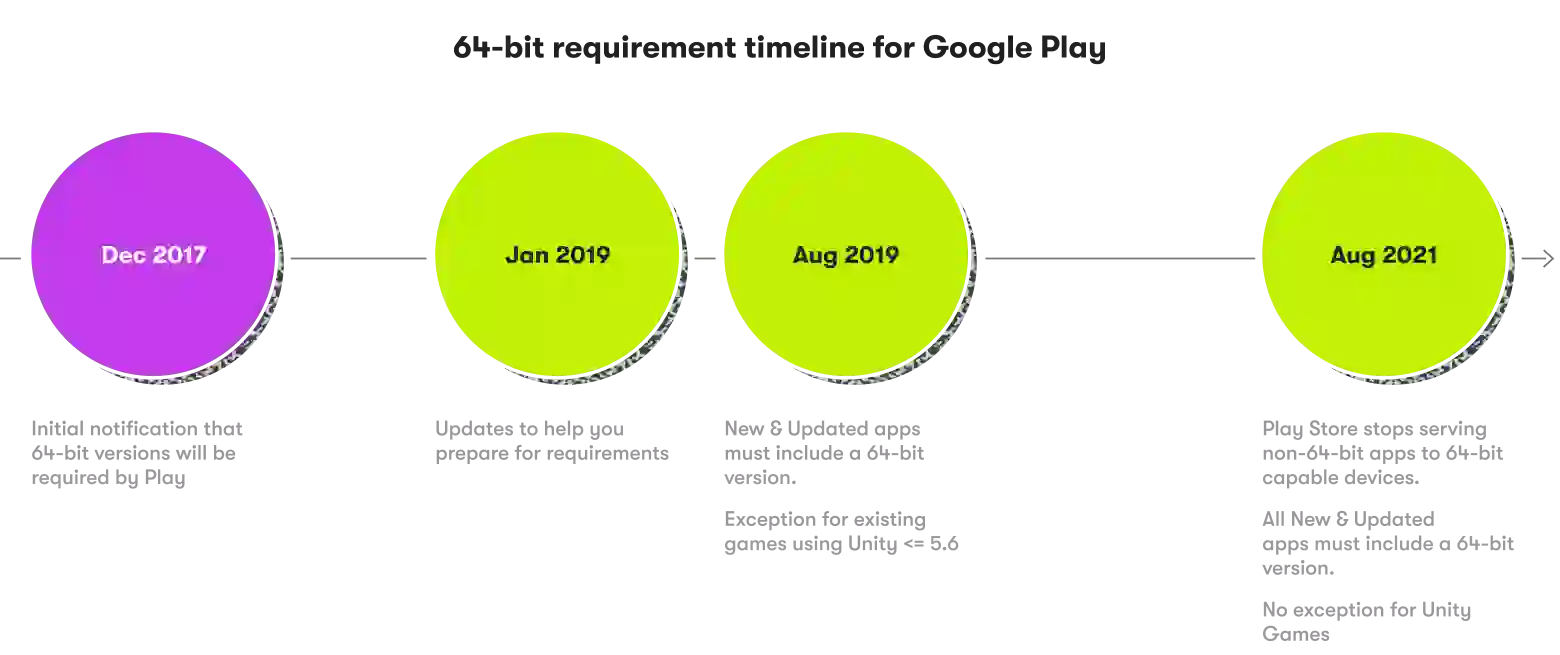
Back in 2017, Google Play notified developers that all applications using 32-bit native libraries should start delivering corresponding 64-bit versions. This initial notification paved the way for the first fully 64-bit compatible version of Android, which is Android 5.0 Lollipop.
How did the Android OS evolve, why was its evolution crucial, and where does Android stand these days? Pull up a chair and keep reading to learn more!
How it started with 32-bit CPUs
Originally, Android OS was a 32-bit operating system. It required a number of significant updates before the Android OS began working with 64-bit CPUs. Moreover, as recently as in 2021, many games and applications compatible with 32-bit CPUs only were still available on Google Play.
Now, back to the emergence of the first 64 bit Android OS. In 2008, HTC introduced its HTC Dream gadget, which had a 32-bit CPU. It was only as tiny as one of the numerous cores available in the modern Android devices but, back then, a 32-bit CPU was able to run Android 1.0. Some years later, HTC brought another Android gadget to market — the HTC Desire 510 — the first 64-bit compatible Android smartphone.
The Desire 510, however, did not arrive on the market at the right time to reap the benefits of that processor, since there weren't any 64-bit applications. Instead, there were tons of 32-bit Android smartphones, so developers were in no rush to build 64-bit apps. Things started to change, though, once Google Play announced a transition to the 64-bit compatibility version.
5.0 Lollipop, the first 64-bit Android version
As mentioned earlier, Android 5.0 Lollipop was the first fully 64-bit compatible version of Android, launched in 2014.
Three years after presenting it, Google vocalized its demand for support of the 64-bit processor in 2017. It took two years after that to update the whole ecosystem.
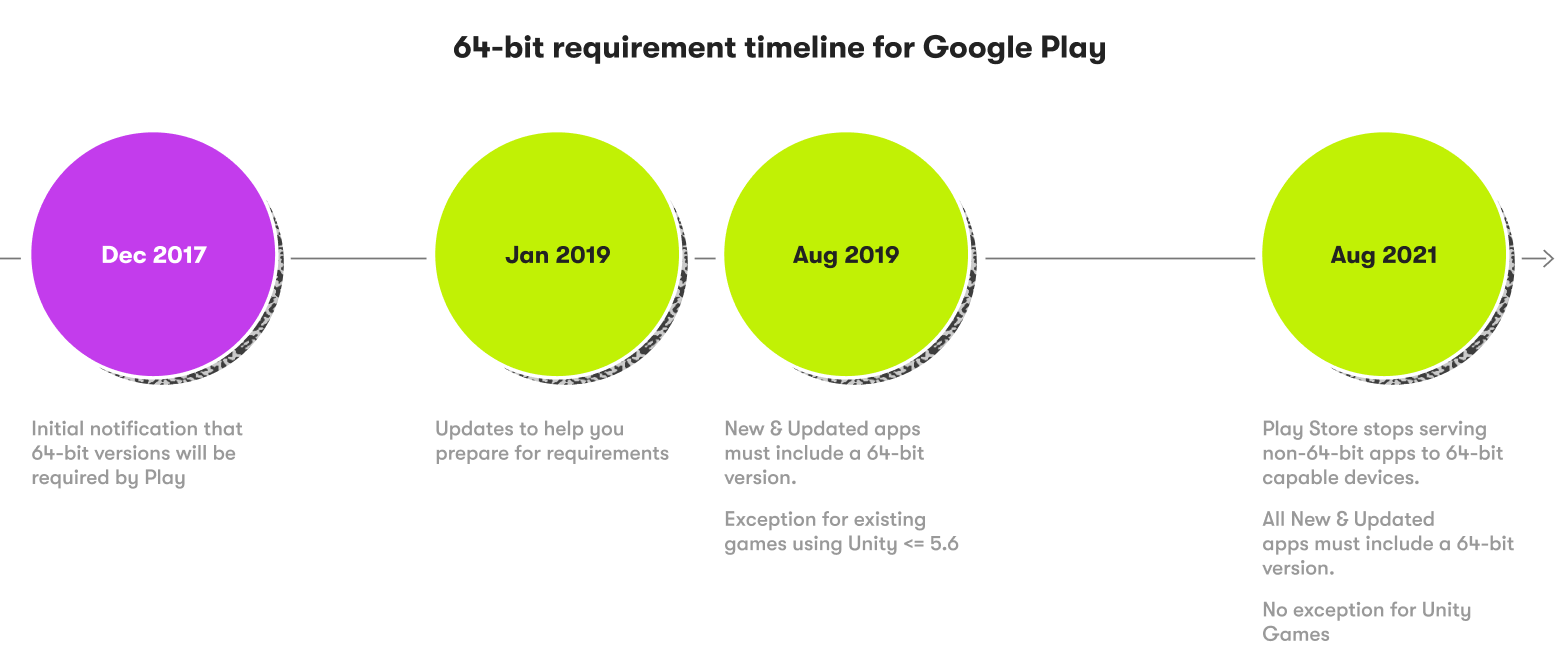
Since introducing the first 64-bit Android version, Google has taken huge steps toward delivering the best experience for all Android users. With the complete shift to 64-bit CPUs, Google will deliver a faster, safer, and more efficient user experience, as well as improved performance overall.
As the next step, new applications and updates rolled out to existing apps on Google Play have to be compatible with 64-bit CPUs to ensure smooth operability with mobile devices that infiltrated the market in 2023.
What 64-bit compatibility brings to the table
Today, nearly 90% of mobile and desktop Android gadgets support 64-bit CPUs (starting from 5.0 Lollipop).
Significant benefits of 64-bit capabilities include the following:
- 64-bit CPUs can manage an extensive amount of data, ensuring that both existing and new technologies will work smoothly on mobile devices.
- 64-bit CPUs can operate better and handle larger fragments of data much faster than a 32-bit processor, which translates into better performance — up to 20% better in some cases.
- 64-bit devices also consistently demonstrate better responsiveness.
Finally, developers will benefit from building their apps for 64-bit Android devices only. This will make development less complex, costly and time-consuming. In addition, developers will benefit from a richer ecosystem.
The demand for 64-bit: what developers need to consider
Key updates that Android developers have to keep an eye on when moving to 64-bit CPUs:
- All applications published on Google Play that contain native code are expected to additionally introduce 64-bit versions.
- Starting in 2021, applications and games that didn't roll out 64-bit versions were restricted from publishing on Google Play.
What's next?
All things considered, the first fully 64-bit compatible version of Android triggered many positive changes and updates starting with its arrival on the scene and continuing to the present time.
With advantages such as the high performance and the safety of the entire Android ecosystem, 64-bit CPUs offer very promising prospects. Besides, the transition will help developers prepare for upcoming innovations, including the emerging immersive mobile and artificial intelligence capabilities.

As Chief Editor, Darya works with our top technical and career experts at EPAM Anywhere to share their insights with our global audience. With 12+ years in digital communications, she’s happy to help job seekers make the best of remote work opportunities and build a fulfilling career in tech.
As Chief Editor, Darya works with our top technical and career experts at EPAM Anywhere to share their insights with our global audience. With 12+ years in digital communications, she’s happy to help job seekers make the best of remote work opportunities and build a fulfilling career in tech.
Explore our Editorial Policy to learn more about our standards for content creation.
read more